351 High Volume Oil Pump Striping Distributor Gear UPDATED
351 High Volume Oil Pump Striping Distributor Gear
Useful information on Gear Pumps
What is a gear pump?
A gear pump is a type of positive displacement (PD) pump. It moves a fluid by repeatedly enclosing a stock-still volume using interlocking cogs or gears, transferring information technology mechanically using a cyclic pumping action. It delivers a smooth pulse-free flow proportional to the rotational speed of its gears.
How does a gear pump work?
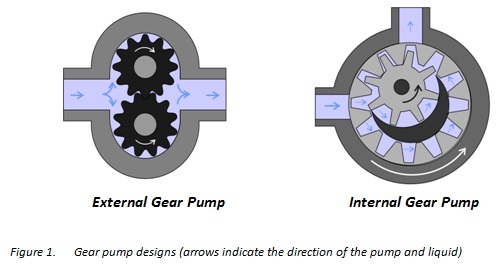
Gear pumps employ the actions of rotating cogs or gears to transfer fluids. The rotating element develops a liquid seal with the pump casing and creates suction at the pump inlet. Fluid, drawn into the pump, is enclosed within the cavities of its rotating gears and transferred to the discharge. There are two basic designs of gear pump: external and internal (Figure 1).
External Gear Pump
An external gear pump consists of two identical, interlocking gears supported by separate shafts. Generally, one gear is driven by a motor and this drives the other gear (the idler). In some cases, both shafts may be driven by motors. The shafts are supported past bearings on each side of the casing.
-
As the gears come up out of mesh on the inlet side of the pump, they create an expanded book. Liquid flows into the cavities and is trapped by the gear teeth equally the gears go on to rotate against the pump casing.
-
The trapped fluid is moved from the inlet, to the discharge, around the casing.
-
As the teeth of the gears get interlocked on the discharge side of the pump, the volume is reduced and the fluid is forced out nether pressure.
No fluid is transferred dorsum through the centre, between the gears, because they are interlocked. Shut tolerances between the gears and the casing allow the pump to develop suction at the inlet and prevent fluid from leaking back from the discharge side (although leakage is more likely with low viscosity liquids).
External gear pump designs can utilize spur, helical or herringbone gears.
Internal gear pump
An internal gear pump operates on the aforementioned principle but the two interlocking gears are of different sizes with i rotating inside the other. The larger gear (the rotor) is an internal gear i.e. it has the teeth projecting on the inside. Inside this is a smaller external gear (the idler – only the rotor is driven) mounted off-eye. This is designed to interlock with the rotor such that the gear teeth engage at 1 indicate. A pinion and bushing attached to the pump casing holds the idler in position. A fixed crescent-shaped partition or spacer fills the void created by the off-centre mounting position of the idler and acts as a seal between the inlet and outlet ports.
-
As the gears come out of mesh on the inlet side of the pump, they create an expanded volume. Liquid flows into the cavities and is trapped by the gear teeth equally the gears proceed to rotate against the pump casing and partitioning.
-
The trapped fluid is moved from the inlet, to the belch, around the casing.
-
Equally the teeth of the gears become interlocked on the discharge side of the pump, the volume is reduced and the fluid is forced out under pressure.
Internal gear pump designs but use spur gears.
What are the main features and benefits of a gear pump?
Gear pumps are compact and simple with a limited number of moving parts. They are unable to match the pressure level generated past reciprocating pumps or the menstruum rates of centrifugal pumps but offer college pressures and throughputs than vane or lobe pumps. Gear pumps are particularly suited for pumping oils and other high viscosity fluids.
Of the two designs, external gear pumps are capable of sustaining higher pressures (upward to 3000 psi) and catamenia rates considering of the more rigid shaft back up and closer tolerances. Internal gear pumps take better suction capabilities and are suited to high viscosity fluids, although they have a useful operating range from 1cP to over ane,000,000cP. Since output is directly proportional to rotational speed, gear pumps are commonly used for metering and blending operations. Gear pumps can be engineered to handle aggressive liquids. While they are commonly fabricated from cast iron or stainless steel, new alloys and composites permit the pumps to handle corrosive liquids such as sulphuric acid, sodium hypochlorite, ferric chloride and sodium hydroxide.
External gear pumps can also be used in hydraulic power applications, typically in vehicles, lifting machinery and mobile institute equipment. Driving a gear pump in opposite, using oil pumped from elsewhere in a organization (commonly by a tandem pump in the engine), creates a hydraulic motor. This is particularly useful to provide power in areas where electrical equipment is bulky, costly or inconvenient. Tractors, for case, rely on engine-driven external gear pumps to power their services.
What are the limitations of a gear pump?
Gear pumps are self-priming and tin can dry-elevator although their priming characteristics improve if the gears are wetted. The gears demand to be lubricated past the pumped fluid and should not exist run dry for prolonged periods. Some gear pump designs tin can be run in either direction so the same pump tin be used to load and unload a vessel, for example.
The close tolerances between the gears and casing mean that these types of pump are susceptible to wear specially when used with abrasive fluids or feeds containing entrained solids. However, some designs of gear pumps, particularly internal variants, allow the treatment of solids. External gear pumps have four bearings in the pumped medium, and tight tolerances, so are less suited to handling abrasive fluids. Internal gear pumps are more robust having only ane begetting (sometimes ii) running in the fluid. A gear pump should always take a strainer installed on the suction side to protect information technology from big, potentially dissentious, solids.
By and large, if the pump is expected to handle abrasive solids it is advisable to select a pump with a college capacity so it tin be operated at lower speeds to reduce vesture. Nonetheless, it should be borne in listen that the volumetric efficiency of a gear pump is reduced at lower speeds and menses rates. A gear pump should not exist operated too far from its recommended speed.
For loftier temperature applications, information technology is of import to ensure that the operating temperature range is compatible with the pump specification. Thermal expansion of the casing and gears reduces clearances inside a pump and this tin also atomic number 82 to increased vesture, and in extreme cases, pump failure.
Despite the best precautions, gear pumps more often than not succumb to clothing of the gears, casing and bearings over time. As clearances increase, at that place is a gradual reduction in efficiency and increase in menstruation slip: leakage of the pumped fluid from the discharge dorsum to the suction side. Flow slip is proportional to the cube of the clearance between the cog teeth and casing so, in do, wear has a small consequence until a critical indicate is reached, from which functioning degrades quickly.
Gear pumps continue to pump against a back pressure and, if subjected to a downstream blockage will go on to pressurise the arrangement until the pump, pipework or other equipment fails. Although most gear pumps are equipped with relief valves for this reason, information technology is always appropriate to fit relief valves elsewhere in the system to protect downstream equipment.
Internal gear pumps, operating at low speed, are mostly preferred for shear-sensitive liquids such as foodstuffs, pigment and soaps. The higher speeds and lower clearances of external gear designs make them unsuitable for these applications. Internal gear pumps are also preferred when hygiene is important considering of their mechanical simplicity and the fact that they are easy to strip down, clean and reassemble.
What are the chief applications for gear pumps?
Gear pumps are usually used for pumping loftier viscosity fluids such equally oil, paints, resins or foodstuffs. They are preferred in whatsoever application where authentic dosing or high pressure output is required. The output of a gear pump is not profoundly affected by pressure and so they also tend to be preferred in any situation where the supply is irregular.
The following table lists some typical applications of external and internal gear pumps:
| Type of gear pump | External | Internal |
| Various fuel oils and lube oils | | |
| Chemical condiment and polymer metering | | |
| Chemical mixing and blending | | |
| Industrial, agronomical and mobile hydraulic applications | | |
| Acids and caustic (stainless steel or blended structure) | | |
| Resins and polymers | | |
| Alcohols and solvents | | |
| Cobblestone, bitumen, and tar | | |
| Polyurethane foam (Isocyanate and polyol) | | |
| Food products: corn syrup, peanut butter, cacao butter, chocolate, sugar, fillers, vegetable fats, vegetable oils, animate being feed | | |
| Paint, inks, and pigments | | |
| Soaps and surfactants | | |
| Glycol | |
Summary
A gear pump moves a fluid by repeatedly enclosing a stock-still volume within interlocking cogs or gears, transferring it mechanically to deliver a smooth pulse-free period proportional to the rotational speed of its gears. In that location are two basic types: external and internal. An external gear pump consists of two identical, interlocking gears supported past separate shafts. An internal gear pump has two interlocking gears of different sizes with 1 rotating inside the other.
Gear pumps are commonly used for pumping high viscosity fluids such every bit oil, paints, resins or foodstuffs. They are also preferred in applications where accurate dosing or high pressure output is required. External gear pumps are capable of sustaining higher pressures (upward to 7500 psi) whereas internal gear pumps have better suction capabilities and are more suited to high viscosity and shear-sensitive fluids.
More info on gear pumps |
|---|
General data |
Send us your enquiry |
Contact us |
DOWNLOAD HERE
351 High Volume Oil Pump Striping Distributor Gear UPDATED
Posted by: peggythoutencers1944.blogspot.com


Comments
Post a Comment